Abstract
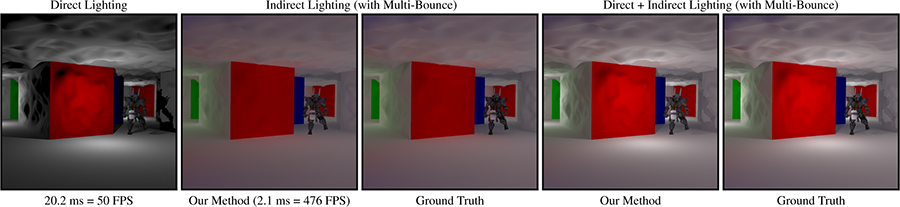
Many rendering algorithms willingly sacrifice accuracy, favoring plausible shading with high-performance. Modular Radiance Transfer (MRT) models coarse-scale, distant indirect lighting effects in scene geometry that scales from high-end GPUs to low-end mobile platforms. MRT eliminates scene dependent precomputation by storing compact transport on simple shapes, akin to bounce cards used in film production. These shapes’ modular transport can be instanced, warped and connected on-the-fly to yield approximate light transport in large scenes. We introduce a prior on incident lighting distributions and perform all computations in low-dimensional subspaces. An implicit lighting environment induced from the low-rank approximations is in turn used to model secondary effects, such as volumetric transport variation, higher-order irradiance, and transport through lightfields. MRT is a new approach to precomputed lighting that uses a novel low-dimensional subspace simulation of light transport to uniquely balance the need for high-performance and portable solutions, low memory usage, and fast authoring iteration.
Copyright Notice
The documents contained in these directories are included by the contributing authors as a means to ensure timely dissemination of scholarly and technical work on a non-commercial basis. Copyright and all rights therein are maintained by the authors or by other copyright holders, notwithstanding that they have offered their works here electronically. It is understood that all persons copying this information will adhere to the terms and constraints invoked by each author’s copyright. These works may not be reposted without the explicit permission of the copyright holder.