Abstract
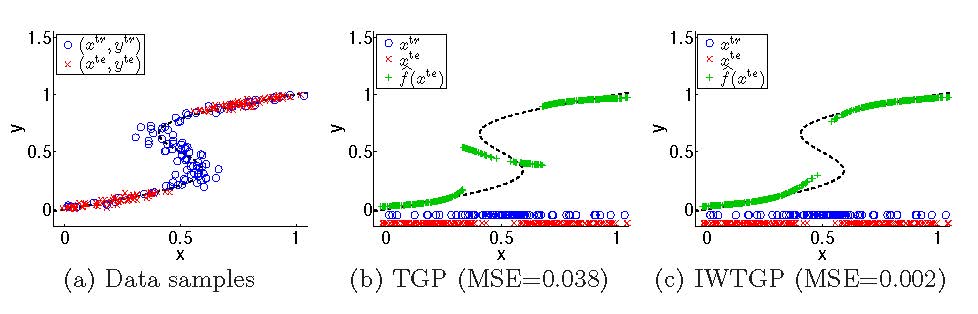
Discriminative, or (structured) prediction, methods have proved effective for variety of problems in computer vision; a notable example is 3D monocular pose estimation. All methods to date, however, relied on an assumption that training (source) and test (target) data come from the same underlying joint distribution. In many real cases, including standard datasets, this assumption is flawed. In the presence of training set bias, the learning results in a biased model whose performance degrades on the (target) test set. Under the assumption of covariate shift, we propose an unsupervised domain adaptation approach to address this problem. The approach takes the form of training instance re-weighting, where the weights are assigned based on the ratio of training and test marginals evaluated at the samples. Learning with the resulting weighted training samples alleviates the bias in the learned models. We show the efficacy of our approach by proposing weighted variants of Kernel Regression (KR) and Twin Gaussian Processes (TGP). We show that our weighted variants outperform their un-weighted counterparts and improve on the state-of-the-art performance in the public (HumanEva) dataset.
Copyright Notice
The documents contained in these directories are included by the contributing authors as a means to ensure timely dissemination of scholarly and technical work on a non-commercial basis. Copyright and all rights therein are maintained by the authors or by other copyright holders, notwithstanding that they have offered their works here electronically. It is understood that all persons copying this information will adhere to the terms and constraints invoked by each author’s copyright. These works may not be reposted without the explicit permission of the copyright holder.