Abstract
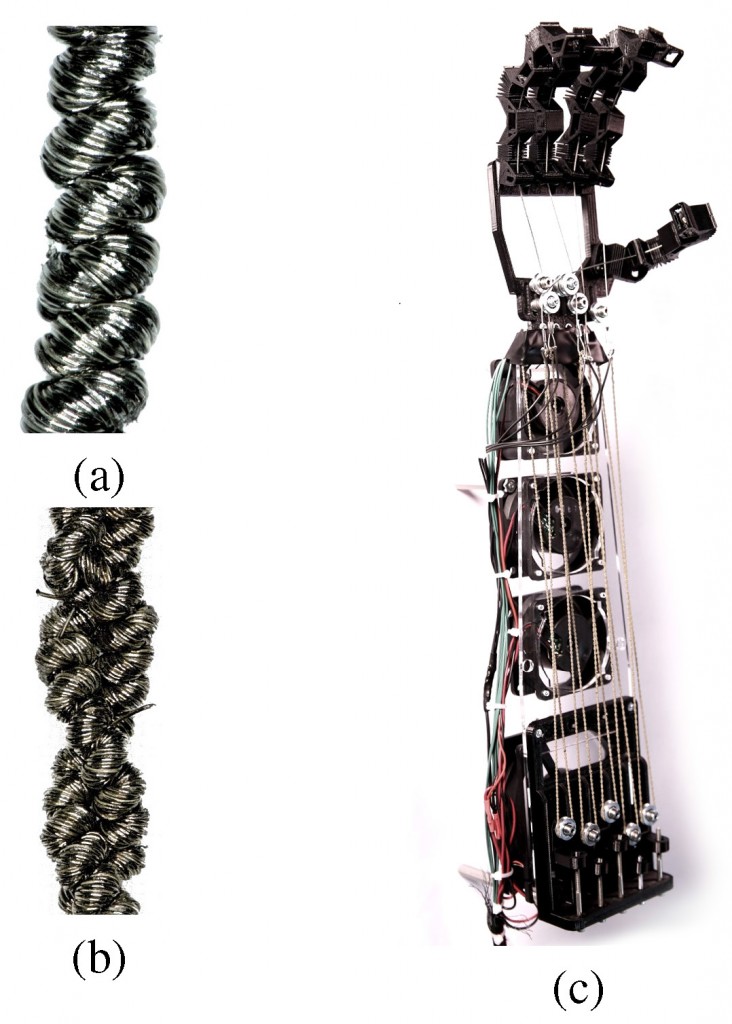
Natural muscles exhibit high power-to-weight ratios, inherent compliance and damping, fast actuation and high dynamic ranges. Unfortunately, traditional robotic actuators have been unable to attain similar properties, especially in a slender muscle-like form factor. Recently, super-coiled polymer (SCP) actuators have rejuvenated the promise of an artificial muscle. Constructed from commercial nylon fishing line or sewing thread and twisted until coils form, these lightweight actuators have been shown to produce significant mechanical power when thermally cycled. In this paper, we develop a thermomechanical and thermoelectric model of SCP actuators and examine their controllability. With off-the-shelf conductive sewing thread, we show the ability to produce controlled forces in under 30 ms, exceeding human muscle performance. Finally, we use SCP actuators in a robotic hand to demonstrate their applicability as a low-cost, high-performance robotic muscle.
Additional Content
Copyright Notice
The documents contained in these directories are included by the contributing authors as a means to ensure timely dissemination of scholarly and technical work on a non-commercial basis. Copyright and all rights therein are maintained by the authors or by other copyright holders, notwithstanding that they have offered their works here electronically. It is understood that all persons copying this information will adhere to the terms and constraints invoked by each author’s copyright. These works may not be reposted without the explicit permission of the copyright holder.